Characteristics
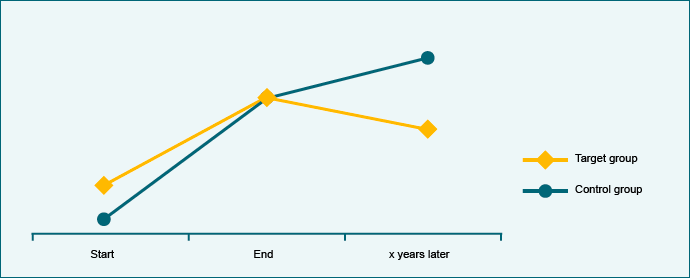
The target group’s development is compared with that of the control group beyond the end of the project.
Example
30% of young mothers in Region x know about the link between clean drinking water and health. That is more than before the project, but less than at the end of the project. The level of knowledge of the control group has progressed from a weak initial position to the level of the target group over the same period, and is continuing to improve.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It can be scientifically proven whether an intervention had a sustainable effect or not. | Data collection is very difficult and requires at least 6 measurements. |
| The approach is methodologically demanding. | |
| There is no measurement of whether the objective has been achieved. |
Suitability
This model is suitable when there needs to be a scientific examination of whether the intervention has had a sustainable effect. It is put to use when there are no reservations about comparisons with control groups and suitable control groups can be defined or constituted. Data about the initial situation might have to be reconstituted. If the initial situation of the control group is not identical with that of the target group, then it is the difference between the target and the control groups that needs to be analysed. Assertions about the effects depend in this case on whether the difference increases or decreases. Due to the time lag, the information becomes available too late for legitimising the project in the short term and for immediate steering and learning. It can, however, be used for the organisation’s long-term development and strategic direction.

