Characteristics
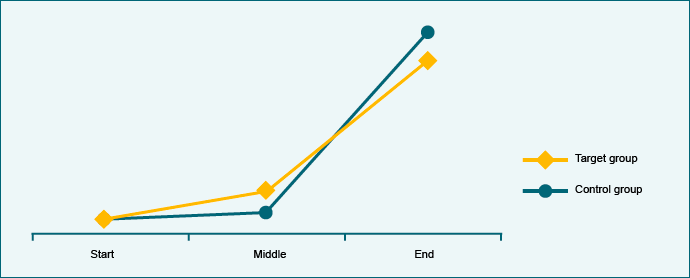
The development of the target group is compared with that of the control group. Additional measurements provide information about the evolution of the project.
Example
90% of children suffering from diarrhoea received successful medical treatment. That is far more than at the start of the project, but the situation of the control group has improved even more over the same duration without any intervention.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| A certain effect can be attributed the intervention or denied. | Data collection is difficult and at least 4 measurements are required. |
| The approach has a sound methodological basis. | This method is methodologically demanding. |
| The achievement of the objectives is not measured. | |
| No assertions can be made about the project’s sustainability. |
Suitability
This model is well suited to legitimising projects, but also for steering and learning inside the organisation. It is used when the effect needs to be proved clearly and there are no ethical reservations about comparisons with control groups. It must be possible to define or constitute suitable control groups.
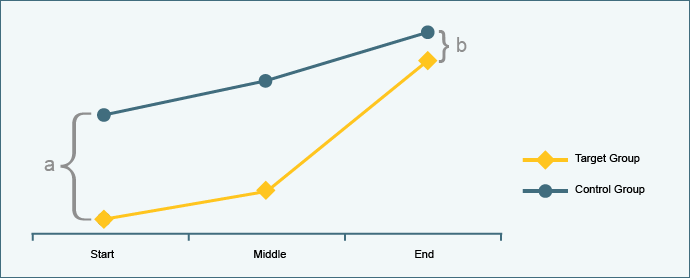
If the initial situation of the control group is not identical with that of the target group, then the difference between the target and the control group must be defined at the start (a) and at the end (b) of the project. The assertion about the effect of the project depends, in this case, whether the difference has increased or decreased. This method is known as “difference in difference”.

