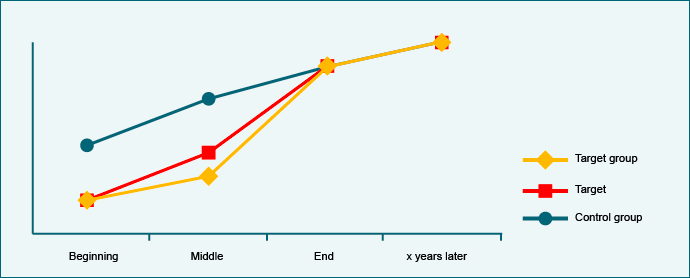
Characteristic
The development of the target group is compared with that of the control group beyond the end of the project and linked to its objectives.
Example
55% of children suffering from diarrhoea received successful medical care. That is 25 percentage points more than before the project. Over the same period, the situation in the control group only improved by 15 percentage points. After the end of the project the development of the target and control groups runs in parallel. The project achieved its target objectives.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It can be scientifically proved whether an intervention was effective and sustained, and whether the objectives were achieved in the long term. | Data collection is very difficult (at least 6 measurements). |
| The approach is methodologically demanding. |
Suitability
This model is suitable for testing the organisation’s long-term development policy and its strategic direction. It is well suited for legitimising the sustainable results towards third parties. Due to the time lag, this approach is less appropriate for immediate steering and learning. It is used whenever sustainable results need to be demonstrated and there are no reservations about comparisons with control groups. One must be able to define or constitute suitable control groups. If the initial situation of the control group is not identical with that of the target group, the difference between the target and control groups must be looked at. Assertions about the effects depend in this case on whether the difference increases or decreases.

